- Most important substance in the bodies of living things.
- Building blocks for muscle, hair, blood cells, skin, slk, enzymes, insulin, etc.
Amino Acids
- Building blocks of proteins.
- Contain an amine (NH2) group and carboxyl (COOH) group.
- Various side chains (R groups) attach to the carbon adjacent to the N.
- Results in 20 different common amino acids.
- Our bodies can synthesize 12 out of 20.
- The other 8 must come from diet
- Known as essential amino acids
 |
| List of Amino Acids |
Polypeptide Chains
- Amino acids joined together with peptide bonds.
- Dipeptides: two amino acids joined together
- Aspartame (artificial sweetener)
- Polypeptides: polymers of many amino acids
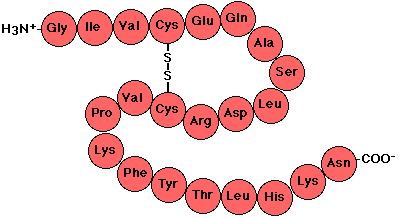 |
| Polypeptide chain or protein |
Proteins
- Polymer of one or more polypeptide chains.
- Some contain several hundred amino acids others several thousand.
- Various structures
Nucleic Acids
 |
| DNA Structure |
- When cells reproduce, they pass genetic information to one another in long-chain molecules called chromosomes.
- Human body contains 46 chromosomes in the nuclei.
- Segments of chromosomes, called genes, carry the coded information to that directs the production of specific polypeptide chains.
- Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acid.
- Three units:
- 5 carbon sugar (ribose or dioxyribose)
- phosphate group
- ring-shaped nitrogen containing base
- There are five possible nitrogen-congaing bases attached to the sugar:
- Adenine (A)
- Cytosine (C)
- Guanine (G)
- Thymine (T)
- Uracil (U)
- DNA has A, C, G, T
- RNA has A, C, G, U
- DNA is two strains coiled around each other in a double helix
- When cells divide, a DNA strand reproduces by first unraveling with the help of enzymes.
- Each of the two resulting strands serves as a template, or pattern, for a new complementary chain.
- Complementary bases on the newly forming strand match the now-exposed bases of the old strand.
- When the process of replication is completed, two identical double-stranded DNA molecules result.
 |
| DNA Replication |
- One strand goes to each half of the dividing cell.
- DNA and RNA molecules instruct cells on how to make proteins.
- DNA is used as a template to make RNA.
- RNA is made up of nucleotides.
- Trinucleotide groups (3 nucleotides) code for various amino acids.
- As the amino acids join together, they form proteins.
- The proteins are the chemical manifestation of our physical characteristics.
 |
| This is an example of protein synthesis from RNA |
Differences between DNA and RNA
- DNA
- the sugar is deoxyribose
- contains thymine
- double strand
- RNA
- the sugar is ribose
- contains uracil
- single strand
No comments:
Post a Comment