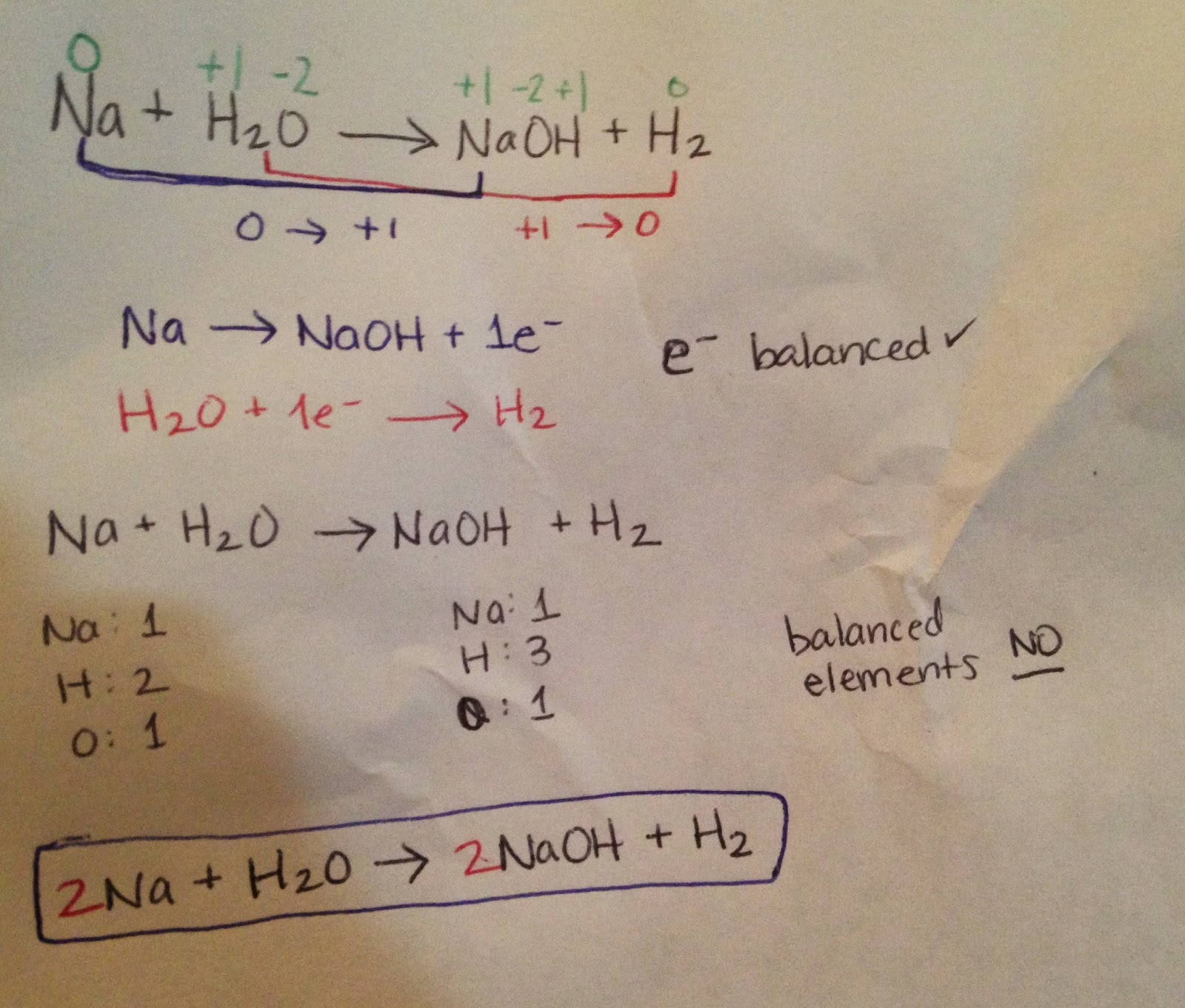- Oxidation-reduction reactions (redox reactions):
- Reactions involving transfers or shifts of electrons
- Oxidation:
- A loss of electrons which makes the oxidation number go up
- Occurs mainly in metals
- Occurs in some covalently bonded substances
- Does not require oxygen (that is not what oxidation means!)
- Reduction:
- A gain of electrons that makes the oxidation number go down (reduced)
- Occurs mainly in nonmetals that gain electrons by taking them from metals
- Review of oxidation numbers:
- Rule 1: free atoms = 0
- Rule 2: ion charge = oxidation number
- Rule 3: compound sum = 0
- Rule 4A: Group 1 = +1
- Rule 4B: Group 2 = +2
- Rule 4C: H = +1 or -1
- Rule 4D: O = -2 or -1
- Rule 4E: Group 17 = -1
- Rule 5: sum of ONs in polyatomic ion = charge
- Practice: Assign Oxidation Numbers
- H2CO3
- H: +1, O: -2, C: +4
- N2
- N: 0
- Zn(OH)4-2
- Zn: +2, H: +1, O: -2
Redox
- Short for reduction-oxidation
- Pronounced “REE-docs”
- Must occur together (An element cannot take electrons without another one losing them.)
- LEO the GERm
- Lose Electrons Oxidation
- Gain Electrons Reduction
- Determine which element is oxidized and which is reduced?
- Zn + 2H+ ➝ Zn2+ + H2
- Zn is oxidized (ON: 0 ➝ +2)
- H+ is reduced (ON: +1 ➝ 0)
- 3Hg2+ + 2 Fe(s) ➝ 3Hg + 2Fe3+
- Hg2+: reduced
- Fe: oxidized
- Oxidizing and Reducing Agents:
- Reducing agent is a substance used to reduce another substance.
- If a substance is oxidized it is the reducing agent.
- Oxidizing agent is a substance used to oxidize another substance.
- If a substance is reduced it is the oxidizing agent.
- Example:
- Zn + 2H+ ➝ Zn2+ + H2
- Zn is oxidized (ON: 0 ➝ +2) [REDUCING AGENT]
- H+ is reduced (ON: +1 ➝ 0) [OXIDIZING AGENT]
- 3Hg2+ + 2 Fe(s) ➝ 3Hg + 2Fe3+
- Hg2+: reduced [OXIDIZING AGENT]
- Fe: oxidized [REDUCING AGENT]
Balancing Redox Reactions
See practice for the procedure, but here are the steps:
- Assign oxidation numbers
- Make half reactions (oxidized reaction and reduced reaction) [forget everything else for now]
- Balance electrons
- Add everything back in and balance traditionally [see Chapter 8 for procedure]